ในยุคที่การพัฒนาแอปพลิเคชันเปลี่ยนไปสู่แนวทาง Reactive มากขึ้น Spring WebFlux กลายเป็นตัวเลือกสำคัญของนักพัฒนา Java ที่ต้องการรองรับการประมวลผลแบบ Asynchronous และ Non-Blocking ซึ่งมีประโยชน์มากเมื่อรับโหลดจำนวนมาก
บทความนี้จะพาคุณไปเรียนรู้การจัดการข้อผิดพลาด (Error Handling) ใน Spring WebFlux โดยใช้แนวทางแบบ Functional ที่ใช้ร่วมกับ RouterFunction และ HandlerFunction ซึ่งต่างจากแนว MVC แบบเดิม
🔍 ทำไมต้องจัดการ Error แบบ Functional?
- เหมาะสำหรับ WebFlux Routing ที่ใช้ RouterFunction
- รองรับ Mono และ Flux ได้อย่างสมบูรณ์
- แยกการจัดการ Error ออกจาก logic หลัก
- รองรับรูปแบบ JSON Response ที่กำหนดเอง
🧱 โครงสร้าง Router และ Handler
@Configuration
public class RouterConfig {
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route(MyHandler handler) {
return RouterFunctions.route()
.GET("/api/hello", handler::hello)
.GET("/api/user/{id}", handler::getUser)
.build();
}
}
@Component
public class MyHandler {
public Mono<ServerResponse> hello(ServerRequest request) {
return ServerResponse.ok().bodyValue("Hello WebFlux!");
}
public Mono<ServerResponse> getUser(ServerRequest request) {
String id = request.pathVariable("id");
if (id.equals("0")) {
throw new NotFoundException("User ID not found");
}
return ServerResponse.ok().bodyValue("User ID: " + id);
}
}
🛑 สร้าง Custom Exception
public class NotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public NotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
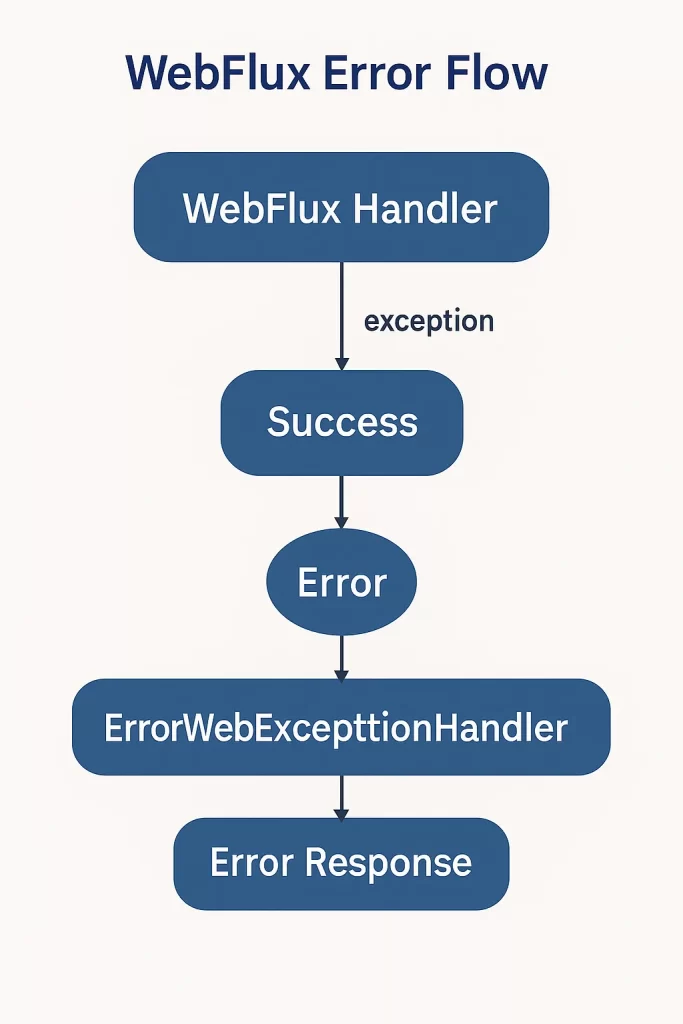
⚙️ สร้าง Global Error Handler
@Component
@Order(-2)
public class GlobalErrorHandler extends AbstractErrorWebExceptionHandler {
public GlobalErrorHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes,
ApplicationContext applicationContext,
ServerCodecConfigurer configurer) {
super(errorAttributes, new WebProperties.Resources(), applicationContext);
super.setMessageReaders(configurer.getReaders());
super.setMessageWriters(configurer.getWriters());
}
@Override
protected RouterFunction<ServerResponse> getRoutingFunction(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return RouterFunctions.route(RequestPredicates.all(), this::renderErrorResponse);
}
private Mono<ServerResponse> renderErrorResponse(ServerRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> errorProps = getErrorAttributes(request, ErrorAttributeOptions.defaults());
return ServerResponse
.status((int) errorProps.getOrDefault("status", 500))
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.bodyValue(Map.of(
"error", errorProps.get("error"),
"message", errorProps.get("message"),
"path", errorProps.get("path"),
"status", errorProps.get("status")
));
}
}
✨ Custom ErrorAttributes (Optional)
@Component
public class CustomErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(ServerRequest request, ErrorAttributeOptions options) {
Throwable error = getError(request);
return Map.of(
"message", error.getMessage(),
"error", error.getClass().getSimpleName(),
"timestamp", Instant.now().toString(),
"status", 500
);
}
}
💬 ตัวอย่าง Response เมื่อเกิด Error
{
"error": "NotFoundException",
"message": "User ID not found",
"status": 500,
"path": "/api/user/0"
}
🌐 ใช้ร่วมกับ WebClient
webClient.get()
.uri("/external-api")
.retrieve()
.onStatus(HttpStatus::is4xxClientError, resp ->
Mono.error(new RuntimeException("Client error")))
.onStatus(HttpStatus::is5xxServerError, resp ->
Mono.error(new RuntimeException("Server error")))
.bodyToMono(String.class);
📊 สรุปแนวทาง
- แยก Logic Error ออกจาก Handler อย่างชัดเจน
- ปรับแต่งรูปแบบ Error Response ได้ตามต้องการ
- ไม่ต้องพึ่ง @ControllerAdvice แบบใน MVC
- ทำงานร่วมกับ Mono/Flux ได้ลื่นไหล
📸 ภาพประกอบแนะนำ
- WebFlux Error Lifecycle
- GlobalErrorHandler Diagram
- Custom Error Response Flow
🔎 คำค้น SEO
Spring WebFlux Error Handling, Functional Router WebFlux, GlobalErrorWebExceptionHandler, Spring Boot Reactive Exception, Spring ErrorAttributes Custom, JSON error response Spring WebFlux, Spring WebFlux Mono Flux Error, Functional Exception Flow