บทความก่อนหน้านี้ ทำให้เราได้พอที่จะเข้าใจ concept ของการใช้วาน Cypress กันมาบ้างแล้ว บทความนี้จะขอกล่าวถึงเรื่องการ Assertion Expect Case ต่าง ๆ ว่าเขียนอย่างไร และสามารถทำอยากที่เราต้องการได้หรือไม่
อธิบายการ Assertions ของ Automated Testing
assertion (การยืนยัน) ในทางงาน test คือการยืนยันการตรวจสอบของสิ่งที่กำลังสนใจ กับผลลัพธ์ที่คาดหวัง
describe('My First Test', () => {
it('Does not do much!', () => {
expect(true).to.equal(true)
})
})
สร้างไฟล์ my-first-test.spec.js เขียนโค๊ดการเทสง่าย ๆ จากนั้นใส่ assertion expect(true).to.equal(true) โดย true แรกคือการที่เราจะแทนค่าที่เรากำลังสนใจที่จะตรวจสอบ true ค่าที่ 2 คือผลลัพธ์ที่ต้องการให้เป็นผลลัพธ์สำหรับการเทสในเงื่อนไขนี้
BDD Assertions
การทดสอบ case scenario ก่อนการเริ่มเขียนโค๊ดจริง ที่เพิ่มการคาดหวังทดสอบ ในเรื่องพฤษติกรรมของทำงานของ website cypress ใช้ library ของ Chaijs Assertion Library (Expect/Should) ที่มีพร้อมครบในเรื่องการทำ assertion case ต่าง ๆ
const person = {
name: 'Poolsawat',
friends: [
{ name: 'Jane' },
{ name: 'Poom', age: 30 },
],
cars: [
'Nissan',
'Toyota'
],
getName: () => {
return "Poolsawat"
},
"aa bb" : "Test"
}
// https://github.com/chaijs/chai
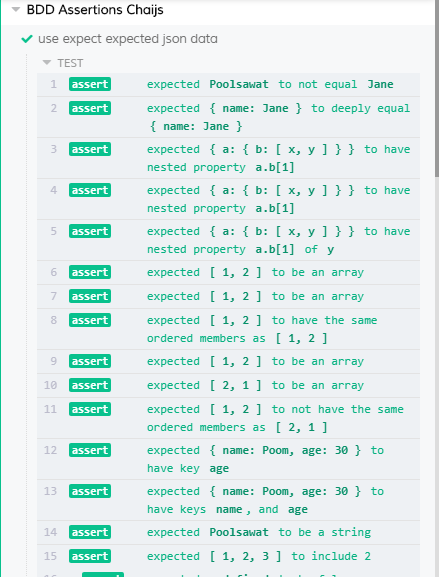
describe('BDD Assertions Chaijs', () => {
it('use expect expected json data', () => {
expect(person.name).to.not.equal('Jane')
expect(person.friends[0]).to.deep.equal({ name: 'Jane' })
expect({ a: { b: ['x', 'y'] } }).to.have.nested.property('a.b[1]')
expect({ a: { b: ['x', 'y'] } }).to.nested.include({ 'a.b[1]': 'y' })
expect([1, 2]).to.have.ordered.members([1, 2]).but.not.have.ordered.members([2, 1])
expect(person.friends[1]).to.have.any.keys('age')
expect(person.friends[1]).to.have.all.keys('name', 'age')
expect(person.name).to.be.a('string')
expect([1, 2, 3]).to.include(2)
expect(undefined).to.not.be.ok
expect(true).to.be.true
expect(false).to.be.false
expect(null).to.be.null
expect(undefined).to.be.undefined
expect(person['aa bb']).to.exist
expect([]).to.be.empty
expect(arguments).to.be.arguments
expect(42).to.equal(42)
expect({ name: 'Jane' }).to.deep.equal({ name: 'Jane' })
expect({ name: 'Jane' }).to.eql({ name: 'Jane' })
expect(10).to.be.greaterThan(5)
expect(10).to.be.at.least(10)
expect(5).to.be.lessThan(10)
expect('test').to.have.length.of.at.most(4)
expect(7).to.be.within(5, 10)
expect([1, 2, 3]).to.be.instanceOf(Array)
expect(person).to.have.property('name')
expect(person).to.have.deep.property('friends')
expect('test').to.have.ownProperty('length')
expect({ a: 1 }).to.have.ownPropertyDescriptor('a')
expect('test').to.have.lengthOf(4)
expect('testing').to.match(/^test/)
expect('testing').to.have.string('test')
expect({ pass: 1, fail: 2 }).to.have.keys('pass', 'fail')
const fn = () => {
throw Error
}
//expect(fn).to.throw(Error)
expect(person).to.respondTo('getName')
//expect(person).itself.to.respondTo('name')
expect(1).to.satisfy((num) => { return num > 0 })
expect(1.5).to.be.closeTo(1, 0.5)
expect([1, 2, 3]).to.include.members([3, 2])
expect(2).to.be.oneOf([1, 2, 3])
//expect(fn).to.change(obj, 'val')
//expect(fn).to.increase(obj, 'val')
//expect(fn).to.decrease(obj, 'val')
})
})
| Chainer | Example |
|---|---|
| not | expect(name).to.not.equal('Jane') |
| deep | expect(obj).to.deep.equal({ name: 'Jane' }) |
| nested | expect({a: {b: ['x', 'y']}}).to.have.nested.property('a.b[1]')expect({a: {b: ['x', 'y']}}).to.nested.include({'a.b[1]': 'y'}) |
| ordered | expect([1, 2]).to.have.ordered.members([1, 2]).but.not.have.ordered.members([2, 1]) |
| any | expect(arr).to.have.any.keys('age') |
| all | expect(arr).to.have.all.keys('name', 'age') |
| a(type) Aliases: an |
expect('test').to.be.a('string') |
| include(value) Aliases: contain, includes, contains |
expect([1,2,3]).to.include(2) |
| ok | expect(undefined).to.not.be.ok |
| true | expect(true).to.be.true |
| false | expect(false).to.be.false |
| null | expect(null).to.be.null |
| undefined | expect(undefined).to.be.undefined |
| exist | expect(myVar).to.exist |
| empty | expect([]).to.be.empty |
| arguments Aliases: Arguments |
expect(arguments).to.be.arguments |
| equal(value) Aliases: equals, eq |
expect(42).to.equal(42) |
| deep.equal(value) | expect({ name: 'Jane' }).to.deep.equal({ name: 'Jane' }) |
| eql(value) Aliases: eqls |
expect({ name: 'Jane' }).to.eql({ name: 'Jane' }) |
| greaterThan(value) Aliases: gt, above |
expect(10).to.be.greaterThan(5) |
| least(value) Aliases: gte |
expect(10).to.be.at.least(10) |
| lessThan(value) Aliases: lt, below |
expect(5).to.be.lessThan(10) |
| most(value) Aliases: lte |
expect('test').to.have.length.of.at.most(4) |
| within(start, finish) | expect(7).to.be.within(5,10) |
| instanceOf(constructor) Aliases: instanceof |
expect([1, 2, 3]).to.be.instanceOf(Array) |
| property(name, [value]) | expect(obj).to.have.property('name') |
| deep.property(name, [value]) | expect(deepObj).to.have.deep.property('tests[1]', 'e2e') |
| ownProperty(name) Aliases: haveOwnProperty, own.property |
expect('test').to.have.ownProperty('length') |
| ownPropertyDescriptor(name) Aliases: haveOwnPropertyDescriptor |
expect({a: 1}).to.have.ownPropertyDescriptor('a') |
| lengthOf(value) | expect('test').to.have.lengthOf(3) |
| match(RegExp) Aliases: matches |
expect('testing').to.match(/^test/) |
| string(string) | expect('testing').to.have.string('test') |
| keys(key1, [key2], […]) Aliases: key |
expect({ pass: 1, fail: 2 }).to.have.keys('pass', 'fail') |
| throw(constructor) Aliases: throws, Throw |
expect(fn).to.throw(Error) |
| respondTo(method) Aliases: respondsTo |
expect(obj).to.respondTo('getName') |
| itself | expect(Foo).itself.to.respondTo('bar') |
| satisfy(method) Aliases: satisfies |
expect(1).to.satisfy((num) => { return num > 0 }) |
| closeTo(expected, delta) Aliases: approximately |
expect(1.5).to.be.closeTo(1, 0.5) |
| members(set) | expect([1, 2, 3]).to.include.members([3, 2]) |
| oneOf(values) | expect(2).to.be.oneOf([1,2,3]) |
| change(function) Aliases: changes |
expect(fn).to.change(obj, 'val') |
| increase(function) Aliases: increases |
expect(fn).to.increase(obj, 'val') |
| decrease(function) Aliases: decreases |
expect(fn).to.decrease(obj, 'val') |
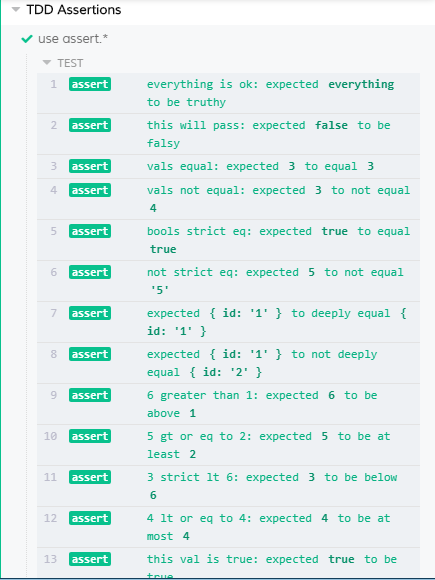
TDD Assertions
คล้ายกับ BDD คือเป็นการเขียน test ต่าง ก่อนการเริ่มเขียน code แต่จะไม่ละเอียดเท่า BDD เพราะไม่รู้ Behavior(พฤติกรรม) ของผู้ใช้งานสามารถใช้ ChaiJs Assert Feature
describe('TDD Assertions', () => {
it('use assert.* ', () => {
assert.isOk('everything', 'everything is ok')
assert.isNotOk(false, 'this will pass')
assert.equal(3, 3, 'vals equal')
assert.notEqual(3, 4, 'vals not equal')
assert.strictEqual(true, true, 'bools strict eq')
assert.notStrictEqual(5, '5', 'not strict eq')
assert.deepEqual({ id: '1' }, { id: '1' })
assert.notDeepEqual({ id: '1' }, { id: '2' })
assert.isAbove(6, 1, '6 greater than 1')
assert.isAtLeast(5, 2, '5 gt or eq to 2')
assert.isBelow(3, 6, '3 strict lt 6')
assert.isAtMost(4, 4, '4 lt or eq to 4')
assert.isTrue(true, 'this val is true')
assert.isNotTrue('tests are no fun', 'val not true')
assert.isFalse(false, 'val is false')
assert.isNotFalse('tests are fun', 'val not false')
//assert.isNull(err, 'there was no error')
assert.isNotNull('hello', 'is not null')
assert.isNaN(NaN, 'NaN is NaN')
assert.isNotNaN(5, '5 is not NaN')
assert.exists(5, '5 is not null or undefined')
assert.notExists(null, 'val is null or undefined')
assert.isUndefined(undefined, 'val is undefined')
assert.isDefined('hello', 'val has been defined')
assert.isFunction(x => x * x, 'val is func')
assert.isNotFunction(5, 'val not funct')
assert.isObject({ num: 5 }, 'val is object')
assert.isNotObject(3, 'val not object')
assert.isArray(['unit', 'e2e'], 'val is array')
assert.isNotArray('e2e', 'val not array')
assert.isString('e2e', 'val is string')
assert.isNotString(2, 'val not string')
assert.isNumber(2, 'val is number')
assert.isNotNumber('e2e', 'val not number')
//assert.isFinite('e2e', 'val is finite')
assert.isBoolean(true, 'val is bool')
assert.isNotBoolean('true', 'val not bool')
assert.typeOf('e2e', 'string', 'val is string')
assert.notTypeOf('e2e', 'number', 'val not number')
})
})
| Assertion | Example |
|---|---|
| .isOk(object, [message]) | assert.isOk('everything', 'everything is ok') |
| .isNotOk(object, [message]) | assert.isNotOk(false, 'this will pass') |
| .equal(actual, expected, [message]) | assert.equal(3, 3, 'vals equal') |
| .notEqual(actual, expected, [message]) | assert.notEqual(3, 4, 'vals not equal') |
| .strictEqual(actual, expected, [message]) | assert.strictEqual(true, true, 'bools strict eq') |
| .notStrictEqual(actual, expected, [message]) | assert.notStrictEqual(5, '5', 'not strict eq') |
| .deepEqual(actual, expected, [message]) | assert.deepEqual({ id: '1' }, { id: '1' }) |
| .notDeepEqual(actual, expected, [message]) | assert.notDeepEqual({ id: '1' }, { id: '2' }) |
| .isAbove(valueToCheck, valueToBeAbove, [message]) | assert.isAbove(6, 1, '6 greater than 1') |
| .isAtLeast(valueToCheck, valueToBeAtLeast, [message]) | assert.isAtLeast(5, 2, '5 gt or eq to 2') |
| .isBelow(valueToCheck, valueToBeBelow, [message]) | assert.isBelow(3, 6, '3 strict lt 6') |
| .isAtMost(valueToCheck, valueToBeAtMost, [message]) | assert.isAtMost(4, 4, '4 lt or eq to 4') |
| .isTrue(value, [message]) | assert.isTrue(true, 'this val is true') |
| .isNotTrue(value, [message]) | assert.isNotTrue('tests are no fun', 'val not true') |
| .isFalse(value, [message]) | assert.isFalse(false, 'val is false') |
| .isNotFalse(value, [message]) | assert.isNotFalse('tests are fun', 'val not false') |
| .isNull(value, [message]) | assert.isNull(err, 'there was no error') |
| .isNotNull(value, [message]) | assert.isNotNull('hello', 'is not null') |
| .isNaN(value, [message]) | assert.isNaN(NaN, 'NaN is NaN') |
| .isNotNaN(value, [message]) | assert.isNotNaN(5, '5 is not NaN') |
| .exists(value, [message]) | assert.exists(5, '5 is not null or undefined') |
| .notExists(value, [message]) | assert.notExists(null, 'val is null or undefined') |
| .isUndefined(value, [message]) | assert.isUndefined(undefined, 'val is undefined') |
| .isDefined(value, [message]) | assert.isDefined('hello', 'val has been defined') |
| .isFunction(value, [message]) | assert.isFunction(x => x * x, 'val is func') |
| .isNotFunction(value, [message]) | assert.isNotFunction(5, 'val not funct') |
| .isObject(value, [message]) | assert.isObject({num: 5}, 'val is object') |
| .isNotObject(value, [message]) | assert.isNotObject(3, 'val not object') |
| .isArray(value, [message]) | assert.isArray(['unit', 'e2e'], 'val is array') |
| .isNotArray(value, [message]) | assert.isNotArray('e2e', 'val not array') |
| .isString(value, [message]) | assert.isString('e2e', 'val is string') |
| .isNotString(value, [message]) | assert.isNotString(2, 'val not string') |
| .isNumber(value, [message]) | assert.isNumber(2, 'val is number') |
| .isNotNumber(value, [message]) | assert.isNotNumber('e2e', 'val not number') |
| .isFinite(value, [message]) | assert.isFinite('e2e', 'val is finite') |
| .isBoolean(value, [message]) | assert.isBoolean(true, 'val is bool') |
| .isNotBoolean(value, [message]) | assert.isNotBoolean('true', 'val not bool') |
| .typeOf(value, name, [message]) | assert.typeOf('e2e', 'string', 'val is string') |
| .notTypeOf(value, name, [message]) | assert.notTypeOf('e2e', 'number', 'val not number') |
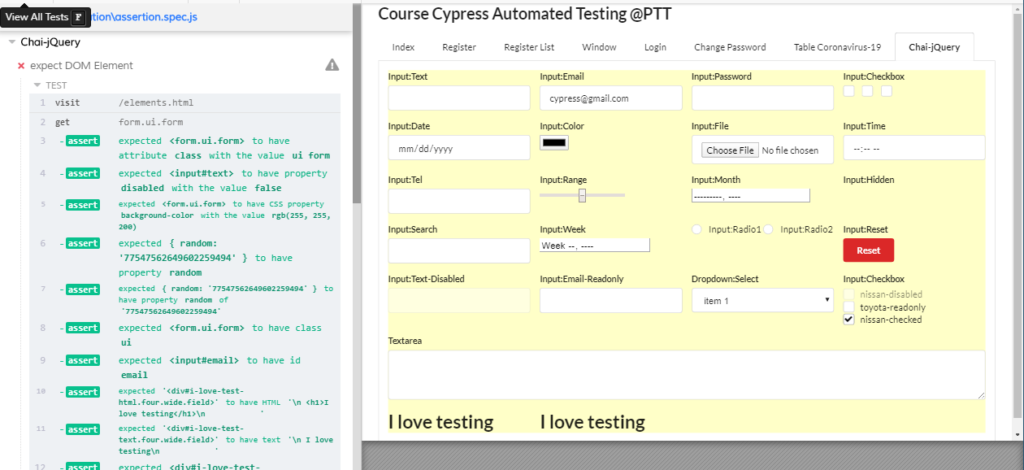
Chai-jQuery
การ assert ส่วนหน้า UI (DOM object) โดยจะใช้คำสั่งการ assert เหล่านี้ หลังจากเรียก command cy.get() หรือ cy.contains()
Cypress.config('baseUrl','https://cypress-testing-143fd.web.app/')
describe('Chai-jQuery', () => {
it('expect DOM Element ', () => {
cy.visit('/elements.html')
.get('form.ui.form').should($el => {
expect($el).to.have.attr('class', 'ui form')
const $notDisabled = $el.find('#text')
expect($notDisabled).to.have.prop('disabled', false)
expect($el).to.have.css('background-color', 'rgb(255, 255, 200)')
expect($el).to.have.data('random', '77547562649602259494')
expect($el).to.have.class('ui')
const $email = $el.find('[name="email"]')
expect($email).to.have.id('email')
const $html = $el.find('#i-love-test-html')
expect($html).to.have.html('\n <h1>I love testing</h1>\n ')
const $text = $el.find('#i-love-test-text')
expect($text).to.have.text('\n I love testing\n ')
expect($text).to.contain('I love testing')
expect($email).to.have.value('[email protected]')
expect($email).to.be.visible
const $hidden = $el.find('[name="hidden"]')
expect($hidden).to.be.hidden
const $option0 = $el.find('#select option:eq(1)')
expect($option0).not.to.be.selected
const $options = $el.find('#select option')
expect($options).to.have.lengthOf(5)
cy.log('lengthOf------------')
const $mazda = $el.find('[name="mazda-checked"]')
expect($mazda).not.to.be.checked
const $focus = $el.find('#text')
//expect($focus).not.to.be.focused
//expect($focus).to.have.focus
expect($focus).to.be.enabled
const $disabled = $el.find('[name="text-disabled"]')
expect($disabled).to.be.disabled
//expect($focus).not.to.be.empty
//expect($nonexistent).not.to.exist
//expect($emptyEl).to.match(':empty')
//expect($el).to.contain('text')
//expect($el).to.have.descendants('div')
})
})
})

| Chainers | Assertion |
|---|---|
| attr(name, [value]) | expect($el).to.have.attr('foo', 'bar') |
| prop(name, [value]) | expect($el).to.have.prop('disabled', false) |
| css(name, [value]) | expect($el).to.have.css('background-color', 'rgb(0, 0, 0)') |
| data(name, [value]) | expect($el).to.have.data('foo', 'bar') |
| class(className) | expect($el).to.have.class('foo') |
| id(id) | expect($el).to.have.id('foo') |
| html(html) | expect($el).to.have.html('I love testing') |
| text(text) | expect($el).to.have.text('I love testing') |
| value(value) | expect($el).to.have.value('[email protected]') |
| visible | expect($el).to.be.visible |
| hidden | expect($el).to.be.hidden |
| selected | expect($option).not.to.be.selected |
| checked | expect($input).not.to.be.checked |
| focus[ed] | expect($input).not.to.be.focusedexpect($input).to.have.focus |
| enabled | expect($input).to.be.enabled |
| disabled | expect($input).to.be.disabled |
| empty | expect($el).not.to.be.empty |
| exist | expect($nonexistent).not.to.exist |
| match(selector) | expect($emptyEl).to.match(':empty') |
| contain(text) | expect($el).to.contain('text') |
| descendants(selector) | expect($el).to.have.descendants('div') |
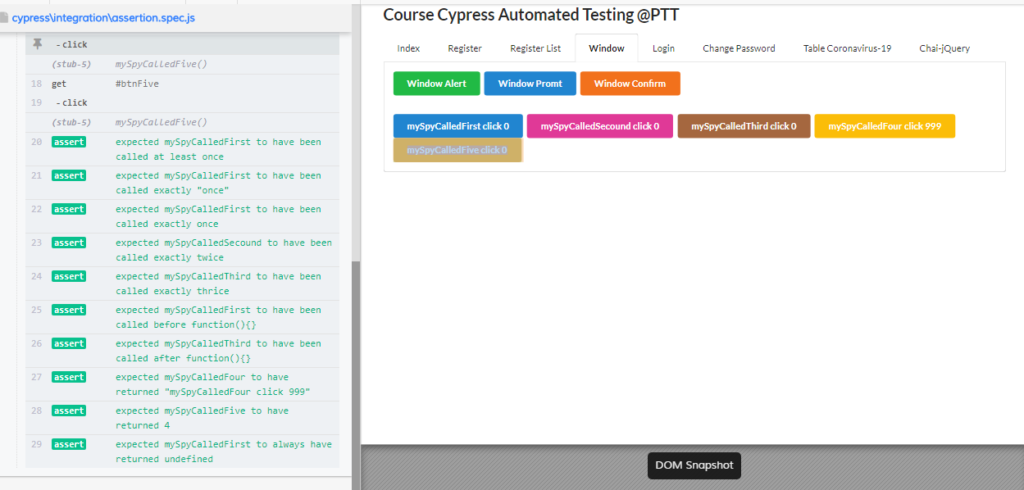
Sinon-Chai
การ assert behavior ของ website event ภายใน ต่าง ๆ ทั้ง window object function (alert ,confirm ,prompt) หรือ custom js function ต่าง ๆ จะใช้ assert spy , stub ตัวอย่างที่สามารถ assert ได้ เช่น มีการ call spy/stub หรือไม่ call กี่ครั้ง จะสามารถเช็คได้ด้วย assert ชุดนี้
Cypress.config('baseUrl','https://cypress-testing-143fd.web.app/')
describe('Sinon-Chai', () => {
it('use sinon expect spy&tub', () => {
let stubFirst ,stubSecound ,stubThird,stubFour,stubFive;
let countStubFiveClick = 0;
cy.visit('/window.html',{
onLoad(win){
stubFirst = cy.stub(win,'mySpyCalledFirst',()=>{})
stubSecound = cy.stub(win,'mySpyCalledSecound',()=>{})
stubThird = cy.stub(win,'mySpyCalledThird',()=>{})
stubFour = cy.stub(win,'mySpyCalledFour',()=>{
return 'mySpyCalledFour click 999'
})
stubFive = cy.stub(win,'mySpyCalledFive',()=> countStubFiveClick+= 2)
}
})
.get('#btnFirst').click()
.get('#btnSecound').click()
.get('#btnSecound').click()
.get('#btnThird').click()
.get('#btnThird').click()
.get('#btnThird').click()
.get('#btnFour').click()
.get('#btnFive').click().get('#btnFive').click()
//.wait(2000)
.then(()=>{
expect(stubFirst).to.be.called
expect(stubFirst).to.have.callCount(1)
expect(stubFirst).to.be.calledOnce
expect(stubSecound).to.be.calledTwice
expect(stubThird).to.be.calledThrice
expect(stubFirst).to.be.calledBefore(stubSecound)
expect(stubThird).to.be.calledAfter(stubSecound)
expect(stubFour).to.have.returned('mySpyCalledFour click 999')
expect(stubFive).to.have.returned(countStubFiveClick)
expect(stubFirst).to.have.always.returned(undefined)
/*expect(stubFirst).to.be.calledWithNew
expect(stubFirst).to.always.be.calledWithNew
expect(spy).to.be.calledOn(context)
expect(spy).to.always.be.calledOn(context)
expect(spy).to.be.calledWith(...args)
expect(spy).to.always.be.calledWith(...args)
expect(spy).to.be.calledWithExactly(...args)
expect(spy).to.always.be.calledWithExactly(...args)
expect(spy).to.be.calledWithMatch(...args)
expect(spy).to.always.be.calledWithMatch(...args)
expect(spy).to.have.thrown(errorObjOrErrorTypeStringOrNothing)
expect(spy).to.have.always.thrown(errorObjOrErrorTypeStringOrNothing)*/
})
})
})
| Sinon.JS property/method | Assertion |
|---|---|
| called | expect(spy).to.be.called |
| callCount | expect(spy).to.have.callCount(n) |
| calledOnce | expect(spy).to.be.calledOnce |
| calledTwice | expect(spy).to.be.calledTwice |
| calledThrice | expect(spy).to.be.calledThrice |
| calledBefore | expect(spy1).to.be.calledBefore(spy2) |
| calledAfter | expect(spy1).to.be.calledAfter(spy2) |
| calledWithNew | expect(spy).to.be.calledWithNew |
| alwaysCalledWithNew | expect(spy).to.always.be.calledWithNew |
| calledOn | expect(spy).to.be.calledOn(context) |
| alwaysCalledOn | expect(spy).to.always.be.calledOn(context) |
| calledWith | expect(spy).to.be.calledWith(...args) |
| alwaysCalledWith | expect(spy).to.always.be.calledWith(...args) |
| calledWithExactly | expect(spy).to.be.calledWithExactly(...args) |
| alwaysCalledWithExactly | expect(spy).to.always.be.calledWithExactly(...args) |
| calledWithMatch | expect(spy).to.be.calledWithMatch(...args) |
| alwaysCalledWithMatch | expect(spy).to.always.be.calledWithMatch(...args) |
| returned | expect(spy).to.have.returned(returnVal) |
| alwaysReturned | expect(spy).to.have.always.returned(returnVal) |
| threw | expect(spy).to.have.thrown(errorObjOrErrorTypeStringOrNothing) |
| alwaysThrew | expect(spy).to.have.always.thrown(errorObjOrErrorTypeStringOrNothing) |
คำสั่ง asserts เหล่านี้ต้องใช้การใช้งาน บ่อย ๆ ถึงจะจำการเรียกใช้งานได้ บทความ ถัดไปจะมาเล่าถึงการใช้งาน spy / stub คอยติดตามด้วยนะครับ